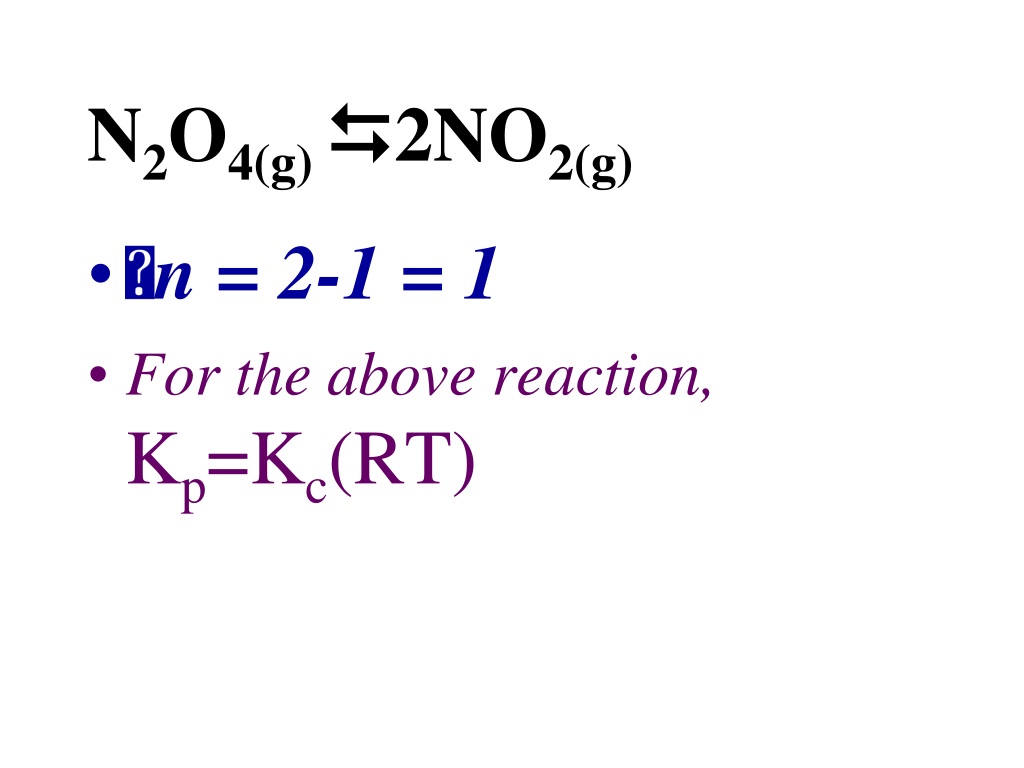Kp Kc Rt N Examples . k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: Kp = kc (rt) d n. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. converting kc to kp and vice versa: when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the.
from www.slideserve.com
for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. Kp = kc (rt) d n.
PPT Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Kp Kc Rt N Examples the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. Kp = kc (rt) d n. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. converting kc to kp and vice versa: K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are:
From slideplayer.com
Chapter 14 Chemical Equilibrium ppt download Kp Kc Rt N Examples Kp = kc (rt) d n. converting kc to kp and vice versa: For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Kp Kc Rt N Examples Kp = kc (rt) d n. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. kc is. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free Kp Kc Rt N Examples R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k.. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Equilibrium Constant PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Kp Kc Rt N Examples Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From slideplayer.com
Chapter 15 Chemical Equilibrium ppt download Kp Kc Rt N Examples converting kc to kp and vice versa: Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. when the number of products. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chemical Equilibrium Q, K, and Calculations Chapter 16 PowerPoint Kp Kc Rt N Examples For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the.. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From brainly.com
Prove the equilibrium law of pressure kp=kc(RT)^delta n Kp Kc Rt N Examples for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 =. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 14 Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free Kp Kc Rt N Examples K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. converting kc to kp and vice versa: the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Kp = kc (rt) d n. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. kc is. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideshare.net
Chapter 15 Lecture Chemical Equilibrium Kp Kc Rt N Examples converting kc to kp and vice versa: K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. Kp = kc (rt) d n. when the. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From es.slideshare.net
EQUILIBRIO QUÍMICO Kp Kc Rt N Examples R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From slideplayer.com
Equilibrium Pressure If the values at equilibrium are given in partial Kp Kc Rt N Examples the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. . Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.youtube.com
Kp=Kc(RT)/🔺n..... YouTube Kp Kc Rt N Examples kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideshare.net
Chemical equilibrium Kp Kc Rt N Examples for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as the ratio of the. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. converting kc to kp and vice versa: K p. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6737691 Kp Kc Rt N Examples R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). when the number of products and reactant molecules is equal, then kc = kp because kp = k (rt)0 = k. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. . Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From brainly.in
write the relation between kp and kc Brainly.in Kp Kc Rt N Examples kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. converting kc to kp and vice versa: for the general reaction aa + bb ⇌ cc + dd, in which all the components are gases, the equilibrium constant expression can be written as. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From www.doubtnut.com
The relationship between Kp and Kc is Kp=Kc(RT)^(Deltan) . What would Kp Kc Rt N Examples For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). K p is equilibrium constant used when equilibrium. Kp = kc (rt) d n. kc is the equilibrium constant for concentrations. when the number of products and. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From slideplayer.com
Chemical Equilibrium Part II Working with K ppt download Kp Kc Rt N Examples Where, δn = (total moles of gas on the. For example, suppose the kc of the reaction between hydrogen and. converting kc to kp and vice versa: k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq). Kp Kc Rt N Examples.
From brainly.in
What is delta n in kp=kc(rt)deltan Brainly.in Kp Kc Rt N Examples k p and k c are the equilibrium constant of an ideal gaseous mixture. R is the ideal gas constant, which is 0.0821 l*atm/ (mol*k). Aa (s) + bb (l) ⇌ gg (aq) + hh (aq) the equilibrium constant expression is written as. the relationship between the two equilibrium constants are: K p is equilibrium constant used when. Kp Kc Rt N Examples.